Kubernetes Demystified and ServiceNow Discovery part1
Summary
What is Kubernetes exactly? If you’re not in the DevOps space it can sound like voodoo. Let’s start with a little history.
Once upon a time, we had to run everything on Physical Hardware and then along came Virtual Machines! Now we can run many isolated servers on a single piece of hardware thanks to products like VMware. However, as time progressed along came an even more light weight option called Containers. Containers offer rapid deployment and are ephemeral in nature. You can build them up and throw them away since the data is typically abstracted from the application. The most widely known example of this is Docker. However, Docker presented a new problem. Managing all of these containers quickly became challenging for large organizations. This is where Kubernetes comes in. It’s purpose is to handle the orchestration and management of all of these containers, including load balancing, scaling and more.
Instant Kubernetes Cluster with K3s
Let’s see this in a real world example. You will need a Linux Host to run your Kubernetes install on. Ubuntu is an easy distro to start with. We will use K3s which is a special lightweight Kubernetes distribution that is certified for production use. In this example we’re running it on a 2GB and 1CPU host.
Install K3s
Open and command shell and paste this in:
sudo curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | K3S_KUBECONFIG_MODE="644" sh -
Thats it! If you run “kubectl cluster-info” it should return some results.
# Install an Nginx webserver to run on our K3s cluster Ingress Copy this Kuberenetes manifest block and paste into your shell.
Now wait a minute or so and browse to the host http://ipddress/web. That’s it, you now have a webserver running in your cluster. You can check the status of your containerized webserver by running: “kubectl get deployments”
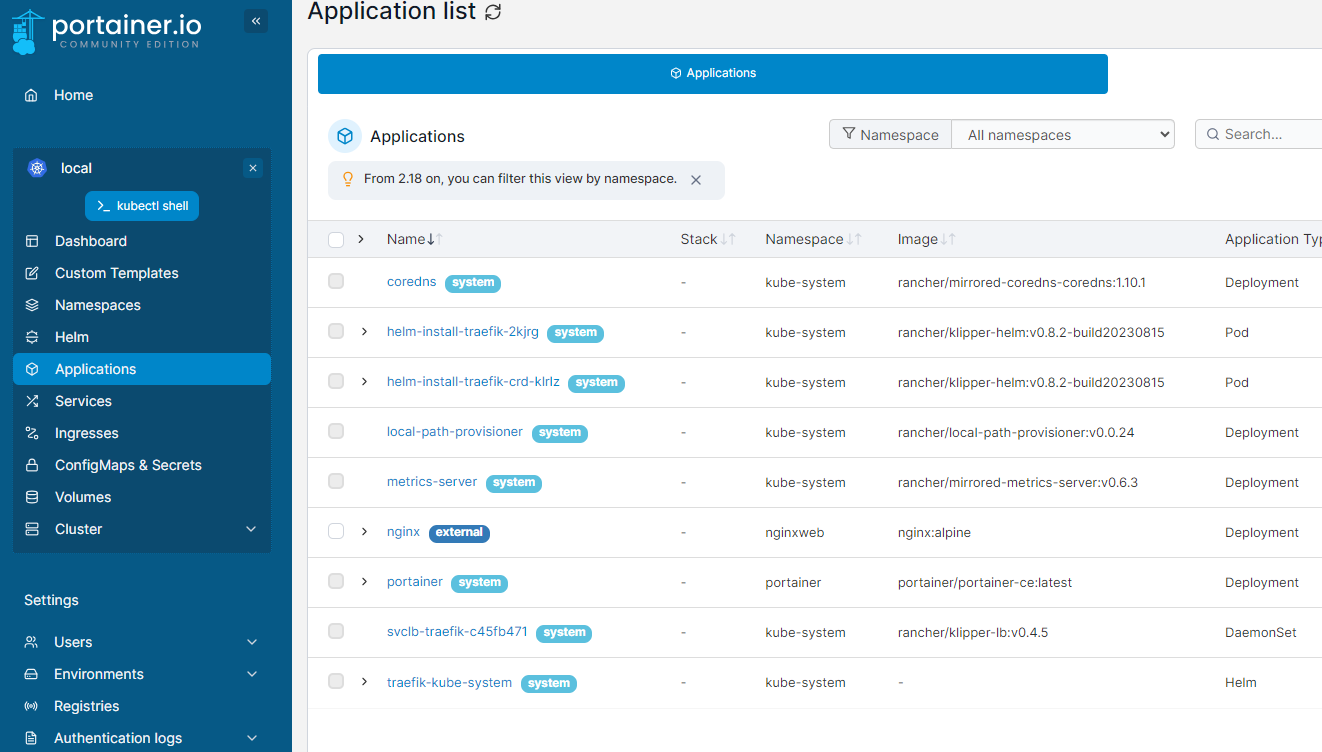
Bonus Management Interface
Portainer is a nice simple add-on for anyone looking to get a Dashboard View. Use this manifest to create.
Now wait a minute or so and browse to the host http://ipddress/portainer. That’s it. Login with admin and set your password.
Leave a comment