Kubernetes Demystified and ServiceNow Discovery part2
Now that we have a Kubernetes Cluster to Discover, lets dive into ServiceNow Kubernetes Discovery. This example assumes you have a MID Server that can connect to the Kubernetes host already.
Create a Kubernetes user with Read Access
We need to create a read only account
Create a user acount in the Kubernetes Cluster
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
#create user
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: k8sadminread
namespace: kube-system
EOF
Create a read only role in the Kubernetes Cluster
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
#create read only cluster role
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: k8s-reader-cluster-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods","configmaps","services","events","namespaces","nodes","limitranges","persistentvolumes","persistenttvolumeclaims","resourcequotas"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
- apiGroups:
- apps
resources: ["*"]
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
EOF
Create the role binding for the read only user in the Kubernetes Cluster
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
#grant user k8s-reader-cluster-role access
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: k8sadminread
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: k8s-reader-cluster-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: k8sadminread
namespace: kube-system
EOF
Creating a Token for the service account in the Kubernetes Cluster
To create a permanent token
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
metadata:
name: k8sadminread-secret
namespace: kube-system
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: k8sadminread
EOF
#now to retrieve token
export NAMESPACE="kube-system"
export K8S_USER_SECRET="k8sadminread-secret"
kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} describe secret $(kubectl -n ${NAMESPACE} get secret | (grep ${K8S_USER_SECRET} || echo "$_") | awk '{print $1}') | grep token: | awk '{print $2}'\n
Testing the Token
Sample to test token with PowerShell 7. In this example the IP is 192.168.1.37.
#requires powershell 7 or newer. Launch as pwsh from command line
$token = "<token copied from previous step>"
$k8sheader = @{authorization="Bearer $($token)"}
Invoke-RestMethod -Method GET -Uri https://192.168.1.37:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=500 -Headers $k8sheader -SkipCertificateCheck | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 10
ServiceNow Kubernetes Discovery
Now onto the ServiceNow side. Preqrequesites
- Ensure the latest version of pattern plugin “sn_itom_pattern” is installed. The Kubernetes patterns are included.
- If the Kubernetes cluster certificate is self signed it will need to be extracted and installed in the midserver java keystore. Use a browser to download the certificate.
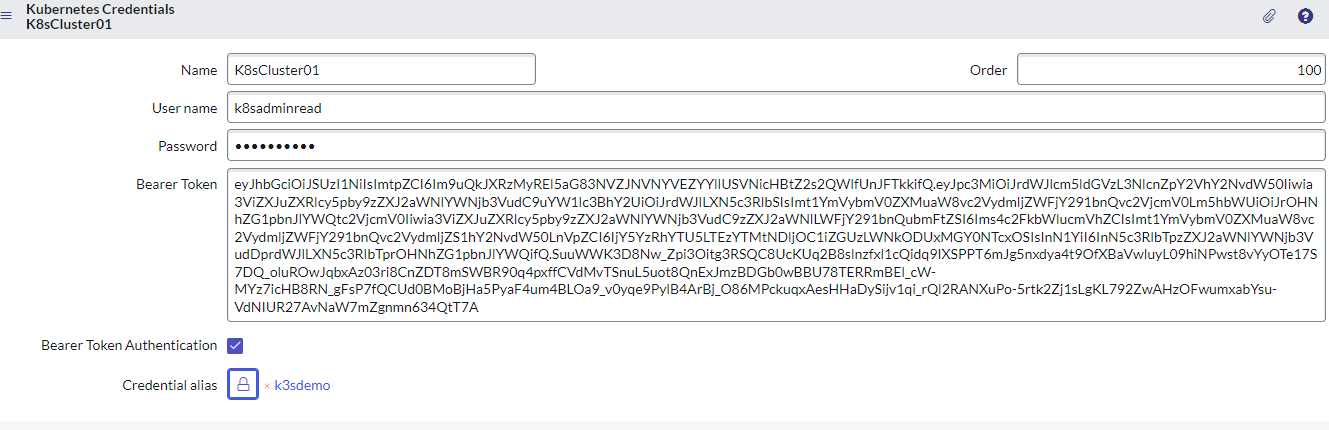
Create Kubernetes Credentials in ServiceNow
- Open Discovery -> Credentials and click new
- Choose Kubernetes Credentials
- Name: K8sCluster01
- Username: k8sadminread
- Bearer Token Authentication: True
- Bearer Token Authentication: copy token generated for the Service account
- Credential alias:
- Select the padlock icon, and then select the search icon.
- On the Connection & Credential Aliases form, select New.
- Specify a name for the credential alias record.
- Define attributes for the alias. Set the Type to Credential.
- Right-click the form header and select Save, then select Update.
- On the Connection & Credential Aliases form, select the newly added alias.
- The alias appears in the Credential alias field.
Create a Serverless Discovery schedule for the cluster
- Open Discovery Schedules -> New
- Name: K8s Discovery Cluster01
- Type: Serverless
- MID Server: select appropriate MID Server
- Save record
- Under Serverless Execution Patterns related list, click New
- Name: K8s Cluster01
- Pattern: Kubernetes
- Save record
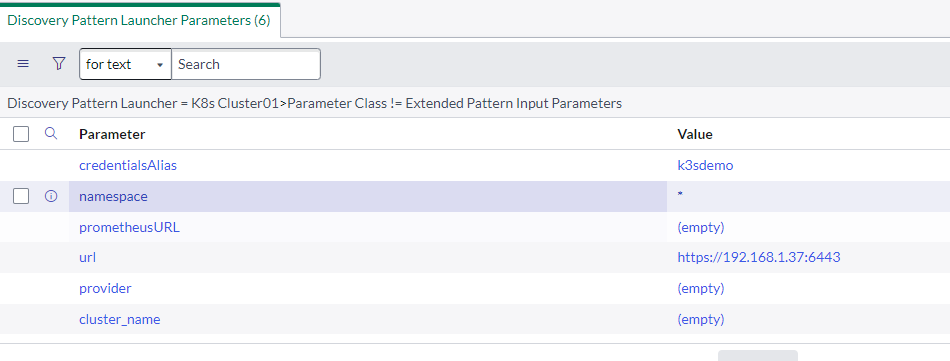
- Within the pattern parameters, set the following:
- credentialsAlias: alias created earlier
- namespace: * (to get all namespaces. Alternatively, you can comma separate, e.g., default, kube-system)
- url: API Master URL
- Save Record
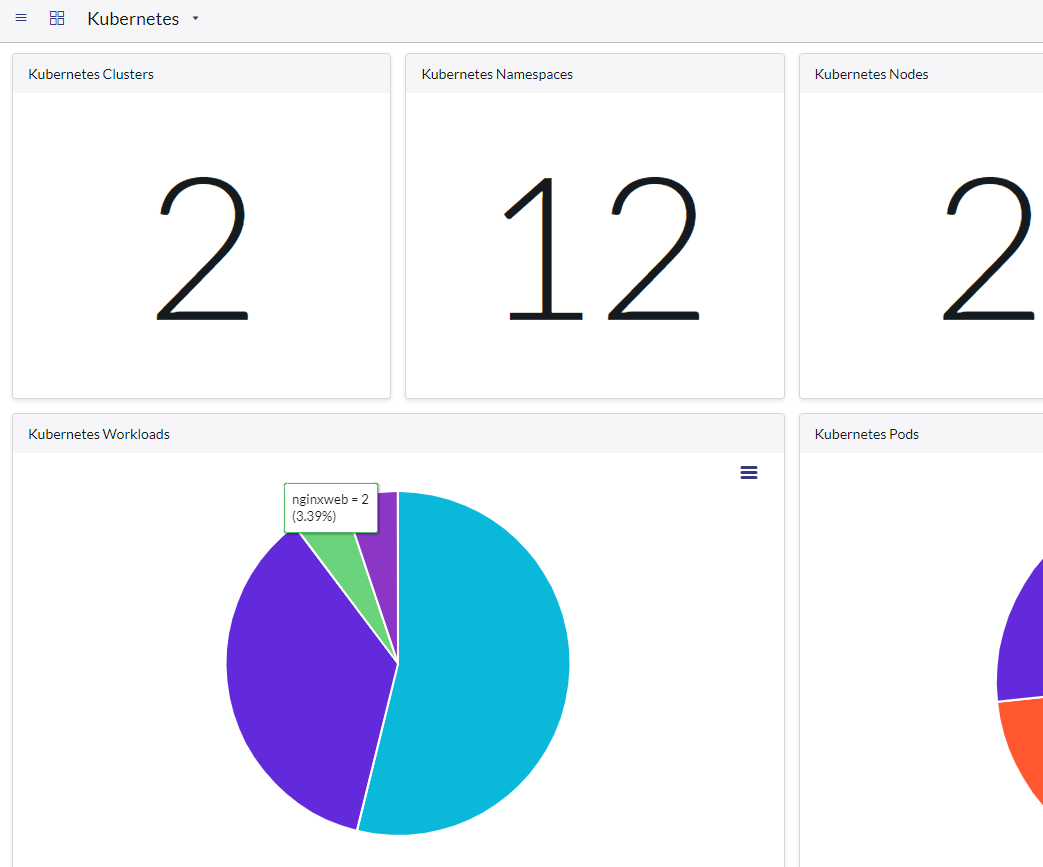
- Run Discover now
- Confirm results and review Kubernetes Dashboard
Tip: If you want to import the K3s Cluster Cert directly into your Windows MID Server
Use this PowerShell 7 script
#Powershell to download and import certificate on MID Server
$MISERVERINSTALLPATH = "C:\winmid\ServiceNow MID Server winmid01"
$KUBEAPI = "https://192.168.1.37:6443/"
$webRequest = [Net.WebRequest]::Create("$KUBEAPI")
try { $webRequest.GetResponse() } catch {}
$cert = $webRequest.ServicePoint.Certificate
$bytes = $cert.Export([Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509ContentType]::Cert)
set-content -value $bytes -encoding byte -path "c:\temp\kubernetes.cer"
cd $MISERVERINSTALLPATH\agent\jre\bin
.\keytool -keystore "$MISERVERINSTALLPATH\agent\jre\lib\security\cacerts" -importcert -storepass changeit -alias k3scert -file "c:\temp\kubernetes.cer" -noprompt
Leave a comment